An Asiana Airlines flight bound for Tokyo experienced an engine failure, prompting its return to Incheon International Airport.
Flight Details
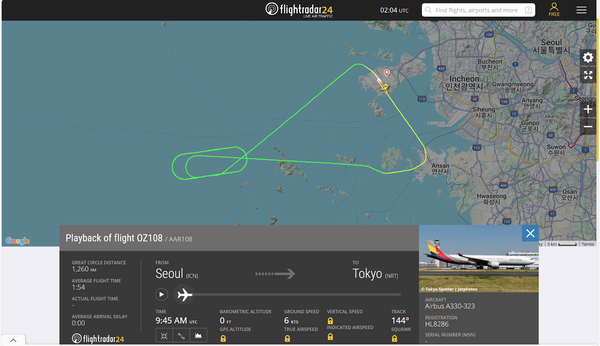
Asiana Airlines flight OZ108 was scheduled from Incheon International Airport (ICN) in Seoul, South Korea to Narita International Airport (NRT) in Tokyo, Japan. The flight was operated on an 11-year-old Airbus A330-300 with registration HL8286. There were 263 passengers on board.
The flight took off at 18:48 KST. However, soon after takeoff, it experienced an engine failure. A witness on the ground, who also managed to take a photo of the aircraft producing dark smoke, reported hearing a loud bang followed by visible flames coming from the left engine.

The aircraft managed to climb to 4200 feet before entering a holding pattern for approximately 20 minutes, likely to dump fuel. The flight landed back at Incheon International Airport safely, 54 minutes after its takeoff.
None of the 263 passengers on board reported any injuries, and at the time of this article, Asiana Airlines is currently working on providing an alternative flight for the passengers.

Asiana Airlines has yet to comment on the details of the incident.
Air Canada Doubles Down on Regional Strength with Major PAL Airlines Expansion » SAS Hosts Air-to-Ground CS:GO Match at 30,000 Feet via Starlink » Portable Charger Catches Fire Mid-Flight, One Passenger Injured »
Comments (0)
Add Your Comment
SHARE
TAGS
NEWS Asiana Engine Failure Asiana Asiana Airlines Engine FailureRECENTLY PUBLISHED
 Why Gogo is Refusing to Join the 'Starlink Speed Race' — And Why It's Winning Anyway
In a recent interview with AeroXplorer, Gogo's SVP Dave Falberg made it clear: Gogo isn't competing in a speed race against Starlink. Rather, it is competing in a race of reliability and integration.
NEWS
READ MORE »
Why Gogo is Refusing to Join the 'Starlink Speed Race' — And Why It's Winning Anyway
In a recent interview with AeroXplorer, Gogo's SVP Dave Falberg made it clear: Gogo isn't competing in a speed race against Starlink. Rather, it is competing in a race of reliability and integration.
NEWS
READ MORE »
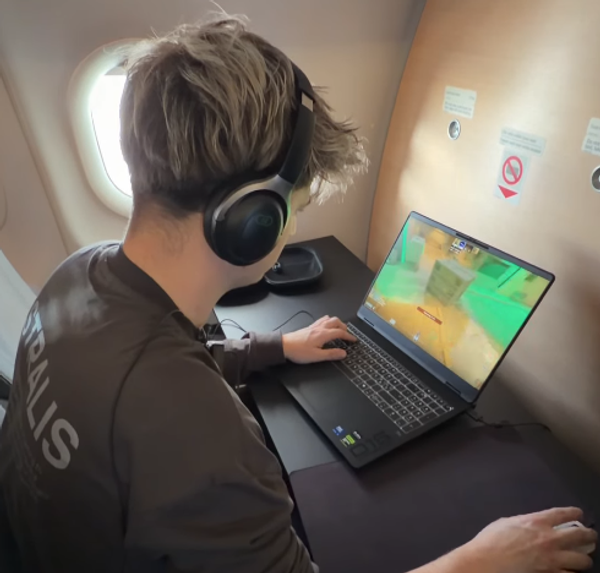 SAS Hosts Air-to-Ground CS:GO Match at 30,000 Feet via Starlink
On January 14, to prove the low-latency capabilities of the SpaceX-powered system, the airline hosted a live multiplayer Counter-Strike video game tournament at 30,000 feet.
NEWS
READ MORE »
SAS Hosts Air-to-Ground CS:GO Match at 30,000 Feet via Starlink
On January 14, to prove the low-latency capabilities of the SpaceX-powered system, the airline hosted a live multiplayer Counter-Strike video game tournament at 30,000 feet.
NEWS
READ MORE »
 Student Education as a Pathway to an Aviation Career
Explore how to become a pilot through aviation degree programs and flight school. Learn about requirements, costs, and career options.
INFORMATIONAL
READ MORE »
Student Education as a Pathway to an Aviation Career
Explore how to become a pilot through aviation degree programs and flight school. Learn about requirements, costs, and career options.
INFORMATIONAL
READ MORE »